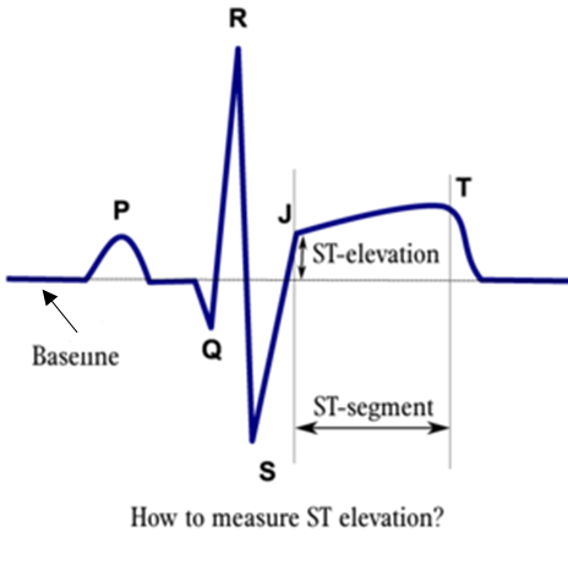
ECG: An Essential Diagnostic Tool
Electrocardiogram (ECG), also known as EKG, is a fundamental diagnostic tool used in cardiology to assess the electrical activity of the heart. This non-invasive test involves placing electrodes on the skin to detect and record the heart’s electrical impulses. The resulting ECG waveform provides valuable insights into the heart’s rhythm and function.
The importance of ECG in cardiac health cannot be overstated. It serves as a primary tool for diagnosing various heart conditions, including arrhythmias, ischemia, and conduction abnormalities. By capturing the electrical activity of the heart in real time, ECG enables healthcare providers to identify cardiac abnormalities, monitor changes in heart rhythm, and guide treatment decisions.
| ECG Component | Description |
|---|---|
| P Wave | Represents atrial depolarization |
| QRS Complex | Indicates ventricular depolarization |
| T Wave | Represents ventricular repolarization |
| PR Interval | Reflects the time for atrial depolarization and conduction through the AV node |
| QT Interval | Represents ventricular depolarization and repolarization |
The role of ECG in cardiac health extends beyond just diagnosing conditions. It plays a crucial role in preventive care by identifying risk factors for cardiovascular disease, evaluating the effectiveness of treatments, and monitoring patients with known heart conditions. Regular ECG screenings can aid in the early detection of abnormalities and help prevent serious complications.
Understanding the significance of ECG in cardiac health is vital for healthcare professionals, paramedical staff, individuals interested in their heart health, and patients with existing heart conditions. By utilizing ECG as an essential diagnostic tool, healthcare providers can enhance the quality of care, improve patient outcomes, and ultimately save lives. For more information on ECG interpretation, visit our article on ECG interpretation.
Understanding Ventricular Tachycardia
Ventricular tachycardia is a serious cardiac arrhythmia characterized by a rapid heartbeat originating from the heart’s ventricles. Understanding the definition and causes of ventricular tachycardia, as well as how this arrhythmia appears on an ECG, is vital for accurate diagnosis and appropriate management.
Definition and Causes of Ventricular Tachycardia
Ventricular tachycardia is defined as a heart rhythm disorder where the heart rate is abnormally fast, typically exceeding 100 beats per minute, and originates from the ventricles rather than the atria. This rapid and potentially life-threatening rhythm disturbance can disrupt the heart’s ability to effectively pump blood, leading to serious complications if not promptly addressed.
The causes of ventricular tachycardia can vary and may include underlying heart conditions such as myocardial infarction, structural heart disease, electrolyte imbalances, or inherited cardiac abnormalities. It can also occur in individuals with a history of heart failure, previous heart surgeries, or those using certain medications that affect cardiac conduction.
How Ventricular Tachycardia Appears on an ECG
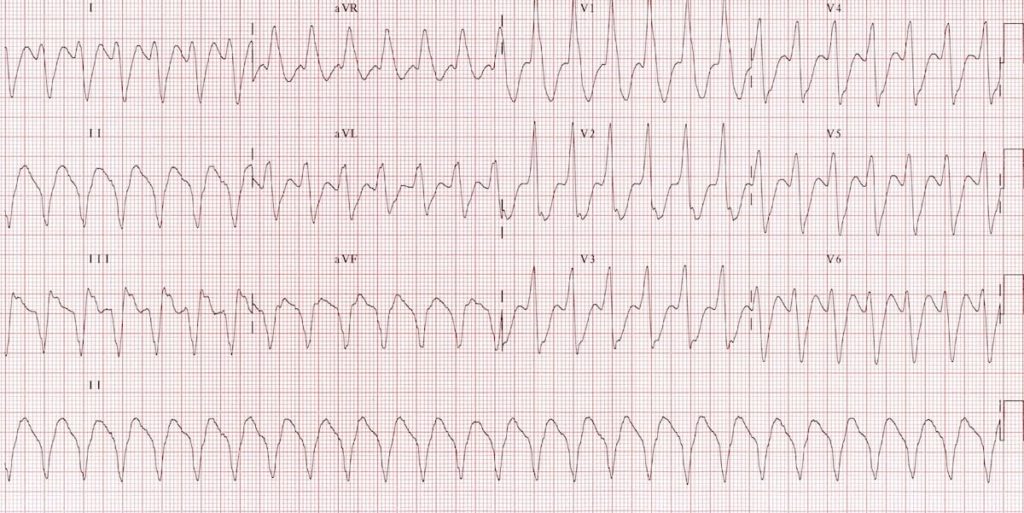
When assessing an electrocardiogram (ECG) for signs of ventricular tachycardia, specific ECG patterns help differentiate this arrhythmia from others. On ECG tracing, ventricular tachycardia is characterized by broad QRS complexes (greater than 0.12 seconds) and a repeating pattern of abnormal ventricular depolarization.
The ECG appearance of ventricular tachycardia may show a regular or irregular rhythm, depending on the underlying mechanism and the specific type of ventricular tachycardia present. Proper recognition of these distinct ECG features is crucial for accurate diagnosis and timely intervention to manage the arrhythmia effectively.
Understanding the definition, causes, and ECG manifestations of ventricular tachycardia is essential for healthcare professionals, as it guides them in the identification and appropriate management of this potentially life-threatening cardiac arrhythmia. For further information on ECG lead placement and interpretation, refer to our articles on ecg lead placement and ecg interpretation.
Role of ECG in Detecting Ventricular Tachycardia
In the realm of cardiac health, the Electrocardiogram (ECG) plays a pivotal role in the detection of Ventricular Tachycardia (VT). This section focuses on the ECG patterns associated with VT and emphasizes the significance of early detection in managing this condition effectively.
ECG Patterns in Ventricular Tachycardia
Ventricular Tachycardia is characterized by specific ECG patterns that indicate rapid and irregular heartbeats originating in the ventricles. On an ECG tracing, VT presents as wide QRS complexes (greater than 0.12 seconds) with absence of P waves. The rhythm is typically regular, but the rate is usually over 100 beats per minute.
| ECG Finding | Description |
|---|---|
| QRS Duration | > 0.12 seconds |
| P Waves | Absent |
| Rhythm | Regular, rate > 100 bpm |
Recognizing these distinct ECG features is essential for accurate diagnosis and prompt intervention in cases of Ventricular Tachycardia.
importance of Early Detection
Early detection of Ventricular Tachycardia through ECG monitoring is critical in preventing potentially life-threatening complications. Rapid and irregular heartbeats can lead to hemodynamic instability, decreased cardiac output, and, in severe cases, degeneration into ventricular fibrillation, a lethal arrhythmia.
By identifying VT early on ECG tracings, healthcare providers can initiate timely interventions such as antiarrhythmic medications, electrical cardioversion, or implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD) placement. These interventions are aimed at restoring normal heart rhythm and reducing the risk of sudden cardiac arrest.
Regular monitoring of high-risk patients through ECG assessments allows for the ongoing evaluation of cardiac health and the timely detection of any arrhythmias, including Ventricular Tachycardia. This proactive approach enables healthcare professionals to intervene promptly and implement appropriate management strategies to improve patient outcomes and prevent adverse cardiac events.
Understanding the role of ECG in detecting Ventricular Tachycardia underscores the importance of leveraging this diagnostic tool for early identification and intervention in patients at risk of arrhythmias. By recognizing the characteristic ECG patterns of VT and emphasizing the significance of early detection, healthcare providers can effectively manage this cardiac condition and safeguard patient well-being.
Interpreting ECG Findings
When analyzing electrocardiogram (ECG) readings, it is essential to accurately differentiate ventricular tachycardia from other types of arrhythmias. Understanding the distinct ECG patterns associated with ventricular tachycardia and recognizing their clinical significance are key aspects in the diagnostic process.
Differentiating Ventricular Tachycardia From Other Arrhythmias
Ventricular tachycardia presents specific ECG characteristics that distinguish it from other arrhythmias. The ECG manifestations of ventricular tachycardia include:
- Wide QRS complexes (greater than 0.12 seconds)
- Regular or irregular rhythm
- Absence of P waves before the wide QRS complexes
- Presence of AV dissociation in some cases
These key ECG features aid in differentiating ventricular tachycardia from supraventricular arrhythmias, such as atrial fibrillation or atrial flutter. While ventricular tachycardia can be life-threatening, prompt recognition through ECG interpretation is vital for appropriate management and intervention.
Clinical Significance of ECG Findings
The ECG findings play a critical role in determining the clinical significance of ventricular tachycardia and guiding treatment decisions. In addition to confirming the presence of ventricular tachycardia, the ECG can provide insights into the underlying cause, severity, and potential complications associated with this arrhythmia.
Moreover, ECG monitoring allows healthcare providers to assess the response to treatment strategies and adjust interventions accordingly. Continuous ECG surveillance is paramount for patients with a history of ventricular tachycardia to monitor their cardiac health status and prevent future cardiac events.
By accurately interpreting ECG findings and recognizing the specific characteristics of ventricular tachycardia, healthcare professionals can effectively diagnose and manage this potentially life-threatening arrhythmia. Regular ECG monitoring and ongoing evaluation are essential components in the comprehensive care of patients with ventricular tachycardia, emphasizing the critical role of ECG in detecting and assessing cardiac abnormalities.
Treatment Approaches
When dealing with ventricular tachycardia, prompt and appropriate treatment is essential to prevent potentially life-threatening complications. Treatment approaches for ventricular tachycardia typically involve a combination of emergency interventions and long-term management strategies to ensure the patient’s well-being.
Emergency Interventions for Ventricular Tachycardia
In cases of ventricular tachycardia, especially those associated with hemodynamic instability or symptoms of reduced perfusion, immediate interventions are crucial. The primary goal of emergency interventions is to restore normal heart rhythm and prevent the progression to more serious arrhythmias like ventricular fibrillation.
| Intervention | Description |
|---|---|
| Cardioversion | The use of electrical energy to reset the heart’s rhythm back to normal. |
| Antiarrhythmic Medications | Drugs such as amiodarone or lidocaine may be administered to help control the abnormal heart rhythm. |
| Intravenous Fluids | Administration of fluids to maintain adequate blood pressure and cardiac output. |
| CPR (Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation) | Initiation of CPR in cases of cardiac arrest associated with ventricular tachycardia. |
Swift and effective response during emergency situations of ventricular tachycardia can significantly improve patient outcomes and reduce the risk of complications.
Long-Term Management Strategies
In addition to emergency interventions, long-term management strategies are essential for individuals with recurrent or persistent ventricular tachycardia. These strategies aim to prevent future episodes, minimize symptoms, and improve overall cardiac health.
| Management Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Medication Therapy | Long-term use of antiarrhythmic medications to help maintain normal heart rhythm and reduce the risk of tachycardia recurrence. |
| Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator (ICD) | For individuals at high risk of sudden cardiac death, an ICD may be implanted to detect and treat life-threatening arrhythmias. |
| Catheter Ablation | A procedure that targets and eliminates the abnormal electrical pathways in the heart responsible for ventricular tachycardia. |
| Lifestyle Modifications | Adoption of heart-healthy habits such as regular exercise, maintaining a balanced diet, and avoiding triggers like excessive caffeine or stress. |
Long-term management strategies play a crucial role in preventing the reoccurrence of ventricular tachycardia and improving the quality of life for individuals with this condition. Regular follow-up appointments and monitoring through ECG tests are also essential to track the effectiveness of treatment and make any necessary adjustments to the management plan.
Preventative Measures
Taking proactive steps to reduce the risk of ventricular tachycardia involves implementing lifestyle changes and regular ECG monitoring to safeguard heart health.
Lifestyle Changes to Reduce Ventricular Tachycardia Risk
Making certain lifestyle modifications can play a critical role in lowering the likelihood of experiencing ventricular tachycardia. By maintaining a heart-healthy lifestyle, individuals can reduce the strain on their heart and minimize the risk of abnormal heart rhythms. Some key lifestyle changes that can help reduce the risk of ventricular tachycardia include:
| Lifestyle Change | Description |
|---|---|
| Regular Exercise | Engaging in moderate physical activity |
| Healthy Diet | Consuming a balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables |
| Weight Management | Maintaining a healthy weight |
| Stress Management | Practicing stress-reducing techniques |
| Limiting Alcohol and Caffeine | Moderating the intake of alcohol and caffeine |
By incorporating these lifestyle changes into one’s daily routine, individuals can promote heart health and reduce the risk factors associated with ventricular tachycardia. For more information on lifestyle interventions to promote heart wellness, consult our article on heart-healthy habits.
Importance of Regular ECG Monitoring
Regular electrocardiogram (ECG) monitoring plays a crucial role in the early detection and management of cardiac abnormalities, including ventricular tachycardia. Routine ECG assessments can provide valuable insights into the heart’s electrical activity, allowing healthcare providers to identify any irregularities promptly.
| Frequency of ECG Monitoring | Recommendation |
|---|---|
| Patients with Known Heart Conditions | Regular ECG monitoring as per healthcare provider’s recommendations |
| Asymptomatic Individuals | Periodic ECG screenings as part of preventative healthcare |
| Post-Treatment Follow-Up | ECG monitoring to assess treatment efficacy and cardiac health |
Regular ECG monitoring is particularly important for individuals with existing heart conditions, as it enables healthcare providers to track changes in heart function and adjust treatment plans accordingly. By prioritizing routine ECG assessments, individuals can actively participate in maintaining their heart health and addressing any potential cardiac issues in a timely manner. For more information on the significance of ECG monitoring, refer to our article on ECG monitoring benefits.