The Importance of ECG Interpretation
Electrocardiograms (ECGs) play a pivotal role in diagnosing various heart conditions, providing invaluable insights into the electrical activity of the heart. Understanding the significance of ECGs and the role of interpreting these diagnostic tests is fundamental in the field of cardiology.
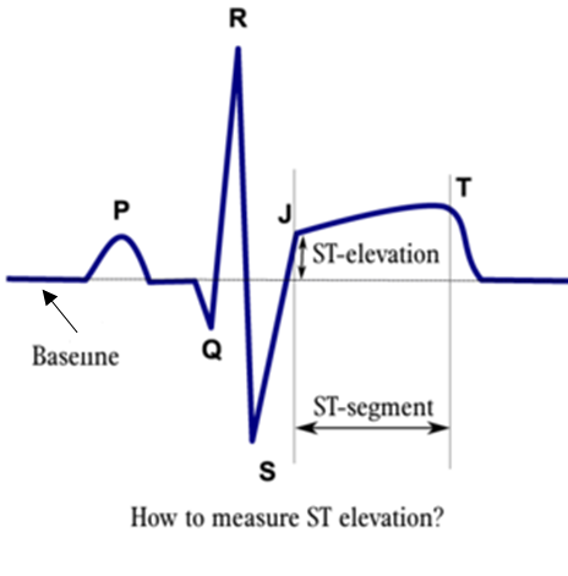
Significance of Electrocardiograms (ECGs)
ECGs are non-invasive tests that record the electrical activity of the heart over a period of time. By capturing the heart’s rhythm and detecting abnormalities in its electrical impulses, ECGs serve as a vital tool in diagnosing a wide range of cardiac conditions. These conditions include arrhythmias, ischemia, infarction, and conduction disorders, among others.
The information derived from an ECG can help healthcare providers assess the overall health of the heart, identify abnormal heart rhythms, and monitor the effectiveness of treatments. ECGs are routinely used in emergency settings, outpatient clinics, and hospitals to aid in the prompt diagnosis and management of cardiac issues.
Role of ECG Interpretation in Diagnosis
Interpreting ECGs is a skill that plays a critical role in diagnosing cardiovascular diseases. Healthcare professionals, including doctors, nurses, and paramedics, must possess the expertise to analyze ECG waveforms accurately. The interpretation of ECGs provides essential information on the heart’s electrical activity, enabling healthcare providers to identify abnormalities and formulate appropriate treatment plans.
By recognizing distinctive ECG patterns associated with various cardiac conditions, healthcare professionals can make informed decisions about patient care. Interpretation of ECGs helps in diagnosing conditions such as arrhythmias, myocardial infarction, and conduction disorders promptly, facilitating timely interventions and improving patient outcomes.
Understanding the importance of ECG interpretation is key to delivering quality cardiac care. Continuous education, practice, and utilization of available resources are essential for enhancing ECG interpretation skills and ensuring accurate diagnosis and management of heart-related conditions. For a detailed discussion on ECG lead placement, check out our article on ecg lead placement.
Basics of ECG Interpretation
To effectively interpret an electrocardiogram (ECG), it is crucial to have a solid understanding of ECG waves and intervals, as well as the ability to differentiate between normal and abnormal ECG patterns.
Understanding ECG Waves and Intervals
ECG waves represent the electrical activity of the heart as it goes through each phase of the cardiac cycle. The main components of the ECG waveform include the P wave, QRS complex, and T wave. Each of these components signifies a specific event in the heart’s electrical conduction system:
- The P wave represents atrial depolarization, signaling the contraction of the atria.
- The QRS complex corresponds to ventricular depolarization, indicating the initiation of ventricular contraction.
- The T wave signifies ventricular repolarization, signifying the end of the electrical activity for that heartbeat.
Additionally, the intervals on an ECG, such as the PR interval and QT interval, provide valuable information about the heart’s electrical properties and the coordination of its chambers.

Interpreting Normal vs. Abnormal ECGs
Differentiating between normal and abnormal ECGs is a fundamental skill in ECG interpretation. A normal ECG demonstrates a consistent pattern of electrical activity that indicates the heart is functioning within normal parameters. In contrast, an abnormal ECG may exhibit irregularities such as:
- Arrhythmias: Irregular heart rhythms that can manifest as tachycardias or bradycardias.
- Ischemia and Infarction: Evidence of insufficient blood flow to the heart muscle (ischemia) or a heart attack (infarction).
- Conduction Disorders: Issues with the electrical conduction system of the heart, leading to abnormalities in the ECG pattern.
By recognizing these abnormalities and understanding their significance, healthcare professionals can provide timely and appropriate interventions for patients with heart conditions. Stay tuned for our upcoming article on ECG ventricular tachycardia to further enhance your understanding of ECG abnormalities.
Enhancing your knowledge of ECG waves and intervals, along with the ability to distinguish between normal and abnormal ECG patterns, is essential for accurate ECG interpretation. By honing these fundamental skills, healthcare professionals can confidently analyze ECGs and contribute to the diagnosis and treatment of cardiovascular conditions.
Common Abnormalities on ECGs
When it comes to interpreting Electrocardiograms (ECGs), healthcare professionals encounter various abnormalities that provide crucial insights into a patient’s cardiac health. Understanding and recognizing common abnormalities on ECGs is essential for accurate diagnosis and timely intervention. The three primary types of abnormalities often seen on ECGs are arrhythmias, ischemia and infarction, and conduction disorders.
Arrhythmias
Arrhythmias refer to irregular heart rhythms that can manifest as a result of various underlying causes. These abnormalities can be categorized as tachyarrhythmias (fast heart rhythms) or bradyarrhythmias (slow heart rhythms). Common types of arrhythmias seen on ECGs include:
- Atrial Fibrillation (AF): Characterized by rapid and irregular atrial contractions.
- Ventricular Tachycardia: Defined by three or more consecutive premature ventricular contractions.
- Atrial Flutter: Marked by rapid regular atrial contractions.
It’s crucial to identify arrhythmias promptly through ECG interpretation to implement appropriate management strategies. For further insight into ventricular tachycardia, refer to our article on ECG ventricular tachycardia.

Ischemia and Infarction
Ischemia and infarction are indicative of insufficient blood supply to the heart muscle, leading to potential damage or cell death. These conditions are commonly assessed through ECG findings, including:
- ST-Segment Elevation: A key marker of acute myocardial infarction (heart attack).
- T-Wave Inversions: Suggestive of myocardial ischemia or injury.
- Pathological Q-Waves: Often seen in past myocardial infarctions.
Timely recognition of ischemic changes on an ECG is critical for initiating appropriate treatment interventions and preventing further cardiac complications. For further information on myocardial infarction as detected by ECG, refer to our article on ECG myocardial infarction.
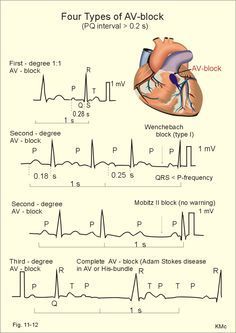
Conduction Disorders
Conduction disorders involve abnormalities in the electrical conduction system of the heart, affecting the timing and coordination of cardiac contractions. These disorders can manifest as:
- Bundle Branch Blocks: Delay or interruption in the electrical impulses along the bundle branches.
- AV Blocks: Impairment in the electrical signals between the atria and ventricles.
- Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome: Presence of an accessory pathway causing abnormal heart rhythms.
Recognition of conduction disorders on an ECG is vital for assessing the risk of potential complications and guiding further diagnostic evaluations. To delve deeper into heart rate calculation methods using an ECG, refer to our article on ECG heart rate calculation.
By familiarizing themselves with these common abnormalities on ECGs, healthcare providers can enhance their diagnostic abilities, provide optimal patient care, and empower patients to prioritize their cardiac health.
Enhancing ECG Interpretation Skills
To excel in electrocardiogram (ECG) interpretation, professionals in the healthcare field must continuously hone their skills and remain updated with the latest developments in this crucial diagnostic process. By focusing on continuous learning, utilizing available resources effectively, and seeking specialist consultations when needed, individuals can enhance their ECG interpretation abilities.
Continuous Learning and Practice
Continuous learning is essential for mastering ECG interpretation. Professionals should dedicate time to study ECG waves, intervals, and common abnormalities to develop a solid foundation. Regular practice with a variety of ECG cases can help improve interpretive skills and build confidence in identifying and analyzing cardiac rhythms accurately.
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Case Studies | Analyzing real-life ECG tracings to understand practical applications. |
| Online Courses | Enrolling in courses focused on ECG interpretation for structured learning. |
| Peer Discussions | Engaging in discussions with colleagues to exchange insights and interpretations. |
Utilizing Resources for Interpretation
Utilizing available resources efficiently can aid in better ECG interpretation. Accessing textbooks, online databases, and ECG simulation tools can provide valuable reference material and practice opportunities. Leveraging advanced technology, such as ECG analysis software, can assist in detecting subtle abnormalities and improving accuracy.
| Resource | Description |
|---|---|
| Textbooks | Reference guides with in-depth explanations of ECG principles and abnormalities. |
| Online Databases | Access to a wide range of ECG cases for practice and learning. |
| ECG Simulation Tools | Interactive platforms for simulated ECG interpretation scenarios. |
By integrating these resources into regular practice sessions, healthcare professionals can reinforce their knowledge and develop proficiency in ECG interpretation.
Seeking Specialist Consultations
In complex cases or when faced with challenging ECG tracings, seeking specialist consultations is imperative. Collaboration with cardiologists, electrophysiologists, or other experts in cardiac care can provide invaluable insights and guidance for accurate interpretation and appropriate management of cardiac conditions.
| Specialist | Expertise |
|---|---|
| Cardiologist | Specialized in diagnosing and treating heart conditions. |
| Electrophysiologist | Focuses on heart rhythm disorders and treatment options. |
| Cardiac Care Team | Multidisciplinary team for comprehensive evaluation and treatment planning. |
Consulting with specialists not only enhances diagnostic accuracy but also fosters a collaborative approach to patient care, ensuring optimal outcomes for individuals undergoing ECG evaluations.
By embracing continuous learning, utilizing diverse resources, and seeking specialist consultations when necessary, healthcare professionals can empower themselves with advanced ECG interpretation skills, ultimately contributing to improved patient care and clinical outcomes.
