How to Read ECG: Reading an electrocardiogram (ECG) is a critical skill for healthcare providers, medical students, and anyone interested in understanding heart health. ECG interpretation involves analyzing the electrical activity of the heart, which helps detect conditions like arrhythmias, myocardial infarctions, and other cardiac abnormalities. This guide will walk you through the essentials of ECG reading, from basic waveforms to advanced interpretation.
Understanding ECG Basics
The ECG, or electrocardiogram, records the heart’s electrical signals and plots them as waveforms on paper or a digital screen. Each segment and wave of an ECG trace provides valuable insights into how the heart is functioning. Understanding these components is the first step in mastering ECG reading.
- P Wave: Represents atrial depolarization (contraction of the atria).
- QRS Complex: Reflects ventricular depolarization, marking the main pumping action of the heart.
- T Wave: Shows ventricular repolarization, a recovery phase of the heart’s electrical cycle.
Each part of an ECG waveform tells a part of the story of the heart’s electrical activity, helping healthcare providers assess both normal and abnormal heart function.
“ECG interpretation transforms lines and waves into life-saving insights about heart health.”
How to Read ECG Waves
Each wave on an ECG strip holds vital clues about heart health. Here’s a breakdown of the core components you should look for when reading an ECG:
- The P Wave: Normally small and rounded, this wave should appear before each QRS complex, indicating the atria are functioning correctly.
- The QRS Complex: This complex represents the main contraction of the heart. It should be narrow and sharp. A widened or unusually shaped QRS complex may signal conduction problems.
- The T Wave: A normal T wave is upright and smooth. An inverted T wave could suggest ischemia or other cardiac issues.
By understanding these core elements, you can begin to detect patterns that signal either healthy or problematic heart rhythms.
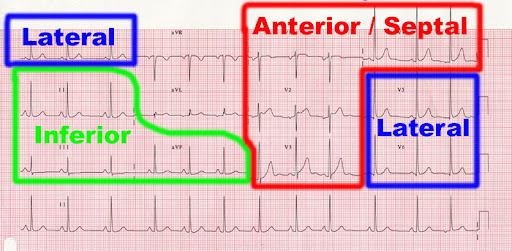
Proper ECG Lead Placement
Correct ECG lead placement is crucial for obtaining accurate readings. Misplaced electrodes can lead to incorrect diagnoses or misinterpretations. Here’s a quick guide to accurate lead placement:
- Chest Leads (V1 to V6): Position these leads across the chest in specific locations to capture the heart’s electrical activity from multiple angles.
- Limb Leads (RA, LA, RL, LL): Attach these leads to the limbs, typically the wrists and ankles, to provide a comprehensive view of the heart.
Using a standardized placement method ensures that the ECG readings accurately reflect the heart’s electrical activity.
Identifying Heart Rhythm and Rate
An essential part of ECG interpretation is identifying the heart’s rhythm and rate. To measure the heart rate from an ECG:
- Locate the R-R Interval: The distance between two consecutive R waves.
- Count the Small Boxes: In a 6-second strip, count the number of R waves and multiply by 10.
This method provides a quick estimate of the heart rate, helping identify whether it’s within a normal range or if arrhythmias are present.
Recognizing ECG Abnormalities
Being able to spot abnormalities is essential in ECG interpretation. Here are some common signs to watch for:
- ST-Segment Elevation: Can indicate a myocardial infarction.
- T-Wave Inversion: Often seen in ischemic heart conditions.
- Prolonged QRS Duration: May suggest a bundle branch block or other conduction issue.
Recognizing these patterns early can enable prompt medical intervention, potentially saving lives.
ST-Segment and T-Wave Analysis for Myocardial Infarction Detection
One of the most crucial applications of ECG is detecting myocardial infarction (heart attack) in its early stages. Key indicators on an ECG include:
- ST-Segment Elevation: This is a primary marker for acute myocardial infarction.
- T-Wave Inversion: Indicates ischemia, often following ST-elevation.
- Pathological Q-Waves: Signifies an old or evolving heart attack and scar tissue.
Interpreting these signs accurately can lead to timely treatment, reducing the risk of long-term damage.
Differentiating Normal vs. Abnormal ECG Patterns
ECG tracings can be classified as normal or abnormal based on specific criteria:
- Normal ECG: Regular rhythm, consistent P-QRS-T waves, and no signs of abnormal deviations.
- Abnormal ECG: Irregular heart rhythms, unusual wave patterns, or abnormal intervals.
Understanding these differences is fundamental to diagnosing heart conditions effectively.
Advanced ECG Interpretation Tips
For healthcare professionals looking to improve their interpretation skills, advanced ECG techniques include:
- Axis Deviation Analysis: Identifying shifts in the heart’s electrical axis, which can indicate ventricular hypertrophy or conduction blocks.
- Bundle Branch Block Recognition: Distinguishing between right and left bundle branch blocks for more precise diagnosis.
- Interval Assessment: Measuring PR, QRS, and QT intervals to detect conduction abnormalities.
These techniques allow for more nuanced readings, which can be essential in complex cases.
Using ECG to Detect Arrhythmias
Arrhythmias, or irregular heart rhythms, are one of the primary issues detected through ECG. Key arrhythmias to watch for include:
- Atrial Fibrillation: Irregular P waves and rapid heart rate.
- Ventricular Tachycardia: Broad QRS complexes with a rapid rhythm.
- Bradycardia: Abnormally slow heart rate, often below 60 beats per minute.
Detecting arrhythmias promptly can help in managing conditions that may otherwise lead to severe complications.
Continuing Education in ECG Analysis
ECG reading is a skill that benefits from continuous practice and learning. Here are resources to further your knowledge:
- Online ECG Courses: Interactive courses for in-depth learning.
- Textbooks on ECG Interpretation: Comprehensive guides to ECG analysis.
- Workshops: Practical sessions focused on hands-on ECG interpretation.
Keeping up-to-date ensures healthcare providers are equipped to handle the latest advances in ECG analysis and cardiac care.
Conclusion: Mastering ECG Interpretation
Learning how to read an ECG is an invaluable skill in healthcare. With practice, you can interpret basic and complex ECG patterns, detect heart abnormalities, and make crucial decisions regarding patient care. Whether you’re just starting out or seeking to advance your skills, a commitment to mastering ECG interpretation will enhance your ability to contribute to effective heart health management.
