Complete Heart Block: A Comprehensive Guide to Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment
Complete heart block, also known as third-degree heart block, is a serious cardiac condition where the electrical signals in the heart are entirely disrupted. This interruption prevents the upper chambers (atria) and lower chambers (ventricles) of the heart from communicating effectively. As a result, the heart cannot pump blood efficiently, leading to symptoms ranging from dizziness to life-threatening cardiac arrest.
Understanding complete heart block is vital because it can be managed effectively with prompt diagnosis and the right treatment plan. This guide will explore the condition in detail, covering its causes, symptoms, diagnostic methods, and treatment options. Whether you’re a healthcare professional, a patient, or someone wanting to learn more, this post provides actionable insights and reliable information.
“Complete heart block can be life-threatening, but timely diagnosis and treatment can lead to excellent outcomes.”
Key Takeaway Highlights
- A complete heart block is a severe disruption in the heart’s electrical signals, causing communication failure between chambers.
- Early symptoms include fainting, fatigue, and a slow heart rate, which can escalate to life-threatening complications.
- Diagnosis often involves electrocardiograms (ECG) and other advanced cardiac monitoring techniques.
- Pacemaker implantation is the most common and effective treatment for managing the condition.
- Regular follow-ups and lifestyle adjustments are critical for maintaining long-term heart health.
What is Complete Heart Block?
Complete heart block is the most severe form of atrioventricular (AV) block, a condition where the heart’s electrical impulses are slowed or completely blocked as they pass from the atria to the ventricles. This results in an uncoordinated contraction between these chambers, drastically reducing the heart’s pumping efficiency.
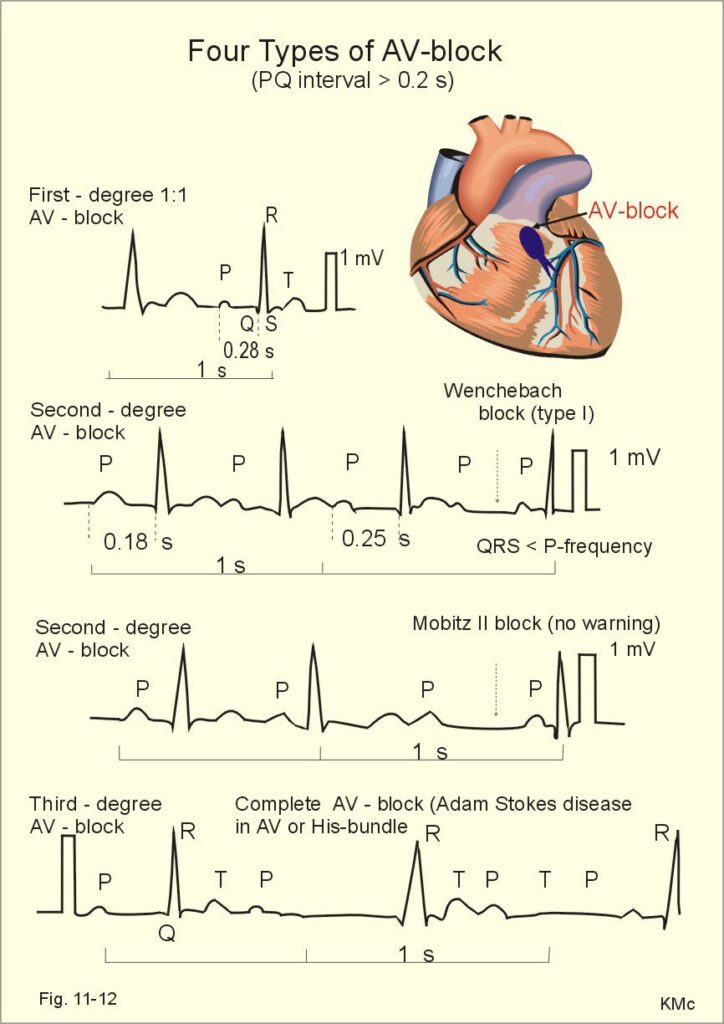
While rare, a complete heart block is considered a medical emergency. It often requires immediate intervention, as prolonged delays can result in severe complications, including heart failure or sudden cardiac death.
Common Causes and Risk Factors
Complete heart block can arise from various underlying causes, including:
- Congenital heart defects: present from birth, especially in children.
- Acquired conditions: such as coronary artery disease, heart attacks, or myocarditis.
- Medications: excessive use of drugs like beta-blockers or calcium channel blockers.
- Degenerative conditions: aging-related changes in the heart’s conduction system.
- Surgical complications: particularly during procedures involving the heart or nearby structures.
Certain populations, such as older adults or individuals with pre-existing heart disease, are at higher risk.
Recognizing the Symptoms
Symptoms of complete heart block vary based on the severity and speed of onset.
- Mild cases: May cause dizziness, fatigue, and shortness of breath.
- Severe cases: fainting (syncope), chest pain, or sudden cardiac arrest.
Monitoring these symptoms and seeking medical attention promptly can prevent escalation.
Diagnosing Complete Heart Block
Diagnosis begins with a thorough clinical evaluation, focusing on
- Patient history: identifying risk factors and symptom patterns.
- Physical exam: listening for irregular heart rhythms or low pulse rates.
Key Diagnostic Tests Include:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): The gold standard for detecting electrical abnormalities in the heart.
- Holter monitoring: continuous ECG recording for 24-48 hours to capture intermittent blocks.
- Echocardiography: Assessing structural abnormalities or underlying heart disease.
These tests provide essential insights into the severity and cause of the block.
Treatment Options: How to Manage Complete Heart Block
Management of a complete heart block depends on its cause, severity, and the patient’s overall health.
Immediate Interventions
- Temporary pacing: Used in emergencies to restore heart rhythm until a permanent solution is found.
- Medications: Administered to stabilize the patient during initial treatment.
Long-Term Solutions
- Permanent pacemaker implantation: the most effective treatment. A pacemaker ensures that the heart maintains a stable rhythm by delivering electrical impulses directly to the ventricles.
Lifestyle Adjustments
Patients with complete heart block should adopt heart-healthy practices:
- Regular follow-ups with a cardiologist.
- Balanced diets are rich in vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
- Avoiding excessive alcohol or tobacco use.
Myths and Misconceptions
Myth 1: Complete Heart Block Only Affects the Elderly
Fact: While more common in older adults, it can also occur in younger populations, especially due to congenital issues or post-surgical complications.
Myth 2: A Pacemaker Fixes Everything Instantly
Fact: While pacemakers are effective, regular monitoring and lifestyle adjustments are still essential.
Myth 3: It’s Always Symptomatic
Fact: In some cases, complete heart block may go unnoticed until complications arise. Routine check-ups can help detect it early.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What causes complete heart block in healthy individuals?
Even healthy individuals can develop heart block due to sudden trauma, viral infections affecting the heart, or rare congenital anomalies.
2. Can a complete heart block be prevented?
While some cases are unpreventable, maintaining overall heart health and managing risk factors can significantly reduce the chances of developing this condition.
3. Is a pacemaker permanent?
Yes, pacemakers are typically permanent solutions, but they may require periodic battery replacements or adjustments.
Summary
A complete heart block is a critical condition requiring immediate medical attention. From identifying early symptoms to undergoing life-saving treatments like pacemaker implantation, understanding this condition can significantly improve outcomes. Proactive health management and regular follow-ups play vital roles in maintaining long-term wellness.
By learning about complete heart block and its treatment options, you’re taking an important step toward empowering yourself or supporting loved ones with this condition.
If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of complete heart block, don’t wait. Consult a cardiologist today for timely evaluation and intervention. For more resources on heart health, explore our other blogs or connect with a heart specialist now!
