Caring for the Heart: Taking care of your heart is one of the most important things you can do for your health. The heart is a vital organ that keeps your body running, and maintaining its health is crucial for a long and happy life. This article will walk you through everything you need to know about caring for your heart, from understanding how it works to practical tips on diet, exercise, and lifestyle changes.
Understanding the Heart
Anatomy of the Heart
The heart is a muscular organ roughly the size of a fist, located slightly left of the center in your chest. It comprises four chambers: two atria and two ventricles. The heart’s rhythmic contractions pump blood through these chambers, supplying your body with oxygen and nutrients.
How the Heart Works
Your heart functions as a pump. It receives deoxygenated blood from the body, pumps it to the lungs for oxygenation, and then sends oxygen-rich blood back out to nourish your organs and tissues. This continuous cycle is vital for sustaining life.
Also Read: Understanding Normal ECG From Waves to Wellness
Common Heart Problems
Coronary Artery Disease
This type of heart disease is the most prevalent because it results from the buildup of plaque in the arteries, which reduces blood flow to the heart muscle.
Heart Attack
A heart attack occurs when a part of the heart muscle doesn’t get enough blood. The more time that passes without treatment, the greater the damage to the heart.
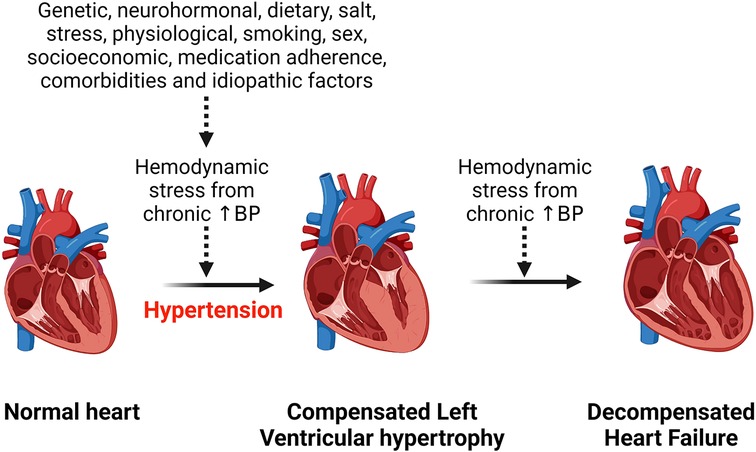
Hypertension
High blood pressure forces your heart to work harder than normal, leading to heart damage over time.
Heart Failure
Heart failure means that the heart isn’t pumping blood as well as it should. It doesn’t mean the heart has stopped working, but it requires medical intervention to manage.
Caring for the Heart: Risk Factors for Heart Disease
Genetic Factors
Your family history can significantly impact your risk of heart disease. If your parents or siblings have heart disease, you might be more at risk.
Lifestyle Factors
Smoking, poor diet, lack of exercise, and excessive alcohol consumption are major lifestyle factors that increase heart disease risk.
Environmental Factors
Stress, pollution, and even certain work conditions can affect your heart health.
Healthy Diet for the Heart
Importance of a Balanced Diet
A heart-healthy diet is low in saturated fats, trans fats, cholesterol, and sodium. It emphasizes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
Foods to Eat
- Fruits and vegetables are rich in vitamins, minerals, and fiber.
- Whole Grains: Oats, whole wheat, and brown rice.
- Lean Proteins: Fish, poultry, beans, and nuts.
- Healthy Fats: Avocados, olive oil, and nuts.
Foods to Avoid
- Processed foods are high in unhealthy fats and sodium.
- Sugary Beverages: Contribute to weight gain and high blood sugar levels.
- Red meat is high in saturated fat and cholesterol.
Exercise and Heart Health
Benefits of Regular Exercise
Regular physical activity strengthens the heart muscle, improves blood circulation, and helps maintain a healthy weight.
Types of Exercises
- Aerobic Exercise: Walking, running, swimming.
- Strength Training: Lifting weights, resistance bands.
- Flexibility Exercises: Yoga, stretching.
How much exercise is needed?
Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous activity each week, plus muscle-strengthening exercises on two or more days a week.
Maintaining a Healthy Weight
Impact of Obesity on Heart Health
Excess weight increases the burden on your heart, raises blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and can lead to diabetes—all risk factors for heart disease.
Tips for Weight Management
- Balanced Diet: Follow a heart-healthy diet.
- Regular Exercise: Stay active.
- Monitor Your Weight: Regularly check your weight and waist circumference.
Avoiding Tobacco and Excessive Alcohol
Effects of Smoking on the Heart
Smoking damages the lining of your arteries, leading to the buildup of fatty material which narrows the artery. It also raises your blood pressure.
Effects of Alcohol on the Heart
Excessive alcohol can lead to high blood pressure, heart failure, and even stroke. Moderation is key.
Tips to Quit Smoking and Limit Alcohol Intake
- Smoking: Seek professional help, use nicotine replacement therapies, and find support groups.
- Alcohol: Limit intake to moderate levels—up to one drink per day for women and two for men.
Managing Stress
How Stress Affects the Heart
Chronic stress may contribute to heart disease by increasing blood pressure and other risk factors.
Stress Management Techniques
- Exercise: Regular physical activity.
- Relaxation Techniques: Meditation, deep breathing exercises.
- Hobbies: Engage in activities that you enjoy and that help you relax.
Regular Health Screenings
importance of Regular Check-ups
Regular health screenings can help detect heart problems early before they become severe.
Key Screenings for Heart Health
- Blood Pressure Checks: At least once every two years.
- Cholesterol Levels: Every four to six years for normal-risk adults.
- Diabetes screening is especially important if you have high blood pressure or other risk factors.

Medications and Heart Health
Common Medications for Heart Disease
Medications may include blood thinners, beta-blockers, ACE inhibitors, and statins, depending on your specific condition.
Importance of Medication Adherence
Taking your medications as prescribed is crucial for managing heart disease and preventing complications.
Recognizing Symptoms of Heart Problems
Warning Signs of a Heart Attack
Symptoms include chest pain or discomfort, shortness of breath, nausea, and lightheadedness.
When to Seek Medical Help
If you experience these symptoms, seek emergency medical help immediately.
Emergency Response to Heart Issues
Immediate Steps to Take During a Heart Attack
Call emergency services, chew an aspirin (if not allergic), and remain calm and seated until help arrives.
CPR and First Aid
Learn CPR and basic first aid to help someone in case of a cardiac emergency.
Long-term Heart Care
Creating a Heart-Healthy Lifestyle
Incorporate healthy habits into your daily routine to support long-term heart health.
Support Systems and Resources
Join support groups, access online resources, and seek guidance from healthcare professionals.
Conclusion
Caring for your heart is a lifelong commitment that involves a combination of healthy eating, regular exercise, stress management, and regular health check-ups. By making these changes, you can significantly reduce your risk of heart disease and enjoy a healthier, more active life.
FAQs
Q: What are the best foods for heart health?
Foods rich in fiber, healthy fats, and lean proteins, like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, nuts, and fish, are excellent for heart health.
Q: How often should I exercise to keep my heart healthy?
Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous activity each week, plus muscle-strengthening exercises twice a week.
Q: Can stress really affect my heart?
Yes, chronic stress can contribute to heart disease by increasing blood pressure and other risk factors.
Q: What are the signs of a heart attack?
Common signs include chest pain, shortness of breath, nausea, and lightheadedness.
Q: How can I quit smoking to improve my heart health?
Seek professional help, use nicotine replacement therapies, and join support groups to aid in quitting smoking.