Understanding ECG Heart Rate Calculation
Exploring the intricacies of ECG heart rate calculation provides valuable insights into the cardiovascular health of individuals. Understanding the significance of ECG heart rate and the basics of ECG measurement is essential for healthcare professionals and individuals monitoring their heart health.
Importance of ECG Heart Rate
The heart rate derived from an ECG, also known as the electrocardiogram, serves as a key indicator of cardiovascular function. It represents the number of heartbeats per minute, reflecting the rhythm of the heart and providing crucial information about cardiac activity. Monitoring ECG heart rate can aid in the early detection of arrhythmias, conduction abnormalities, and other heart conditions, facilitating timely intervention and treatment.
Basics of ECG Measurement
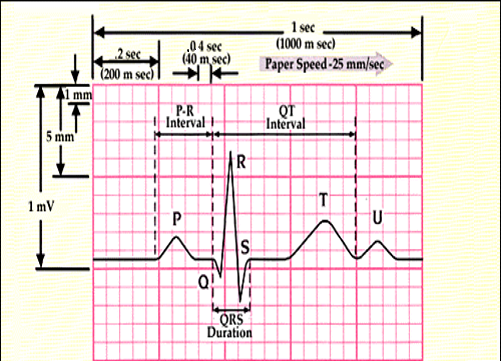
ECG measurement involves recording the electrical activity of the heart using electrodes placed on the body. The ECG waveform comprises various components, each representing a specific aspect of cardiac depolarization and repolarization. By analyzing the ECG tracings, healthcare professionals can assess the heart rate, rhythm, and conduction pathways, offering valuable insights into cardiac health.
In a clinical setting, understanding the basics of ECG measurement is fundamental for accurate interpretation and diagnosis. Different ECG leads provide unique perspectives on the electrical activity of the heart, aiding in the identification of abnormalities such as ventricular tachycardia and myocardial infarction. The knowledge gleaned from ECG readings plays a crucial role in guiding treatment decisions and improving patient outcomes.
By delving into the importance of ECG heart rate and mastering the fundamentals of ECG measurement, healthcare professionals can enhance their diagnostic skills and provide optimal care for patients with cardiovascular concerns. Stay tuned for further insights into ECG interpretation and its clinical applications in our upcoming article on ECG interpretation.
ECG Heart Rate Calculation
In the realm of ECG and cardiac assessments, accurately determining the heart rate from electrocardiogram (ECG) tracings plays a fundamental role in evaluating heart health and identifying potential abnormalities. This section sheds light on the process of determining heart rate from ECG tracings and discusses various methods used for calculating heart rate.
Determining Heart Rate from ECG Tracings
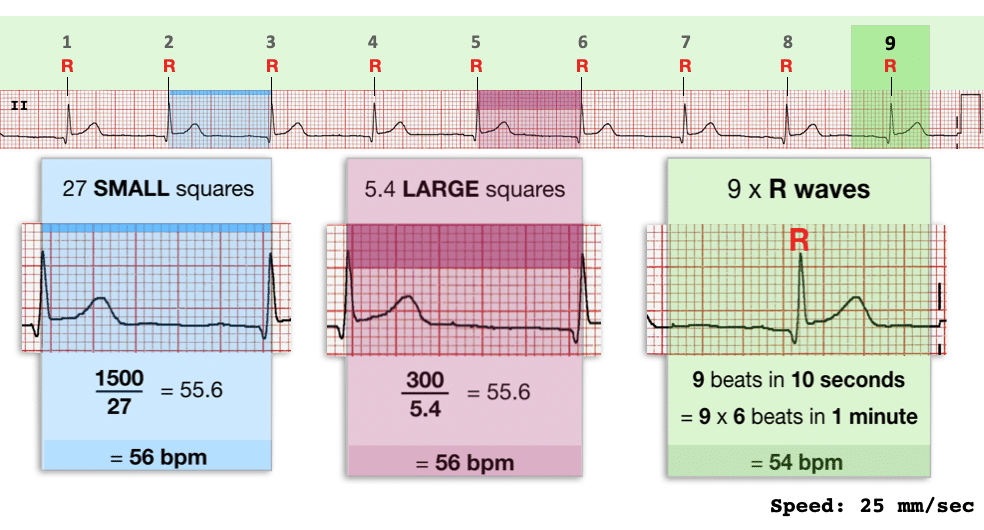
To calculate the heart rate from an ECG trace, clinicians primarily analyze the intervals between QRS complexes, which correspond to ventricular depolarization. The distance between consecutive QRS complexes on the ECG strip provides the time elapsed between each heartbeat. By inversely calculating this time interval, the heart rate in beats per minute (BPM) can be derived.
In addition to manually counting the number of QRS complexes over a specific duration, software programs are utilized in modern clinical settings to automate heart rate calculations from ECG recordings. These digital tools enhance accuracy and efficiency in determining heart rate, particularly in cases where ECG tracings may present complexities.
Calculating Heart Rate Using Different Methods
Various methods exist for calculating heart rate from ECG data, each offering unique insights into cardiac function and rhythm. One common approach is the standard method of measuring the R-R interval, representing the space between two successive R waves on the ECG. By converting this interval to heart rate using the formula HR = 60/(R-R interval in seconds), healthcare professionals can obtain a precise heart rate value.
Another method frequently employed is the utilization of heart rate monitors or devices that directly display heart rate readings based on real-time ECG signals. These portable tools are valuable for continuous heart rate monitoring in clinical settings and during physical activities.
| ECG Heart Rate Calculation Method | Description |
|---|---|
| R-R Interval Measurement | Calculates heart rate based on the time gap between consecutive R waves. |
| Heart Rate Monitors | Directly measure and display heart rate derived from ECG signals. |
| Software Analysis | Automated tools analyze ECG tracings to determine heart rate with precision. |
By employing diverse calculation methods, healthcare providers can accurately assess heart rate dynamics, monitor cardiac conditions, and formulate appropriate treatment strategies. Understanding the nuances of ECG heart rate calculation is paramount in delivering informed care and facilitating comprehensive cardiac evaluations.
Factors Affecting ECG Heart Rate
When analyzing ECG heart rate measurements, several factors come into play that can influence the accuracy and interpretation of the results. Two key factors that significantly impact ECG heart rate calculation are the influence of age on heart rate measurement and the impact of medications and medical conditions.
Influence of Age on Heart Rate Measurement
Age plays a crucial role in determining heart rate values in an ECG reading. As individuals age, changes occur in the cardiovascular system that can affect heart rate. It is essential to consider the normal variations in heart rate at different life stages when assessing ECG traces.
| Age Group | Normal Heart Rate Range (beats per minute) |
|---|---|
| Infants (0-1 year) | 100-160 |
| Children (1-10 years) | 60-140 |
| Adolescents (11-17 years) | 60-100 |
| Adults (18 years and older) | 60-100 |
Understanding the expected heart rate range based on age helps healthcare professionals interpret ECG findings accurately and identify any deviations that may indicate underlying cardiac issues. Variations outside the norm can prompt further investigation and medical intervention if necessary.
Impact of Medicines and Medical Conditions
The use of certain medications and the presence of specific medical conditions can also influence ECG heart rate measurements. Medications such as beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers, and anti-arrhythmic drugs can affect heart rate by either slowing it down or altering the heart’s electrical activity.
Medical conditions such as atrial fibrillation, heart failure, and thyroid disorders can lead to irregular heart rates or abnormalities in the ECG tracings. These conditions can mask the true heart rate or create false readings, complicating the accurate assessment of cardiac health.
It is crucial for healthcare providers to be aware of a patient’s medication history and medical conditions when interpreting ECG results. This knowledge enables them to appropriately adjust for any factors that may impact heart rate calculations and make informed decisions regarding patient care.
By understanding the influence of age, medications, and medical conditions on ECG heart rate measurement, healthcare professionals can ensure the accuracy and reliability of ECG interpretations. Taking these factors into account provides a comprehensive view of a patient’s cardiac health and guides appropriate treatment strategies based on individual circumstances.
Clinical Implications of ECG Heart Rate
When analyzing an electrocardiogram (ECG) report, understanding the heart rate findings and heart rate variability can provide valuable insights into a patient’s cardiac health.
Interpreting Heart Rate Findings in ECG Reports
The heart rate, measured in beats per minute (BPM), is a fundamental parameter assessed in an ECG report. It indicates how efficiently the heart is functioning and can help identify abnormalities in the heart’s rhythm. Normal resting heart rates typically range between 60 and 100 BPM, with variations based on individual factors such as age, fitness level, and underlying medical conditions.
| Heart Rate Category | Heart Rate Range (BPM) |
|---|---|
| Normal | 60 – 100 |
| Bradycardia (Low Heart Rate) | < 60 |
| Tachycardia (High Heart Rate) | > 100 |
Interpreting the heart rate findings in an ECG report involves comparing the recorded heart rate with the standard ranges and assessing any deviations from the norm. An abnormally high or low heart rate can indicate various cardiac issues that may require further investigation and treatment.
Significance of Heart Rate Variability in Diagnosis
Heart rate variability (HRV) is the variation in time intervals between successive heartbeats. It reflects the autonomic nervous system’s influence on the heart and is considered a marker of cardiac health and overall well-being. Reduced HRV has been associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular events and mortality.
Assessing HRV in an ECG provides valuable information about the heart’s ability to adapt to physiological demands and environmental stressors. By analyzing the patterns and fluctuations in heart rate over time, healthcare providers can gain insights into the patient’s cardiovascular health, autonomic function, and risk of developing cardiac complications.
Understanding the clinical implications of heart rate findings and heart rate variability in ECG reports is essential for healthcare professionals in diagnosing and managing various cardiac conditions. By leveraging this information, clinicians can make informed decisions regarding treatment strategies, risk assessment, and patient care, ultimately promoting better heart health outcomes.