Understanding ECG Lead Placement
In the realm of electrocardiography (ECG), the precision of lead placement plays a pivotal role in acquiring accurate and reliable results for diagnosing cardiac conditions. Understanding the significance of correct ECG lead placement and having a fundamental grasp of ECG leads are essential components of conducting a successful ECG analysis.
Importance of Proper ECG Lead Placement
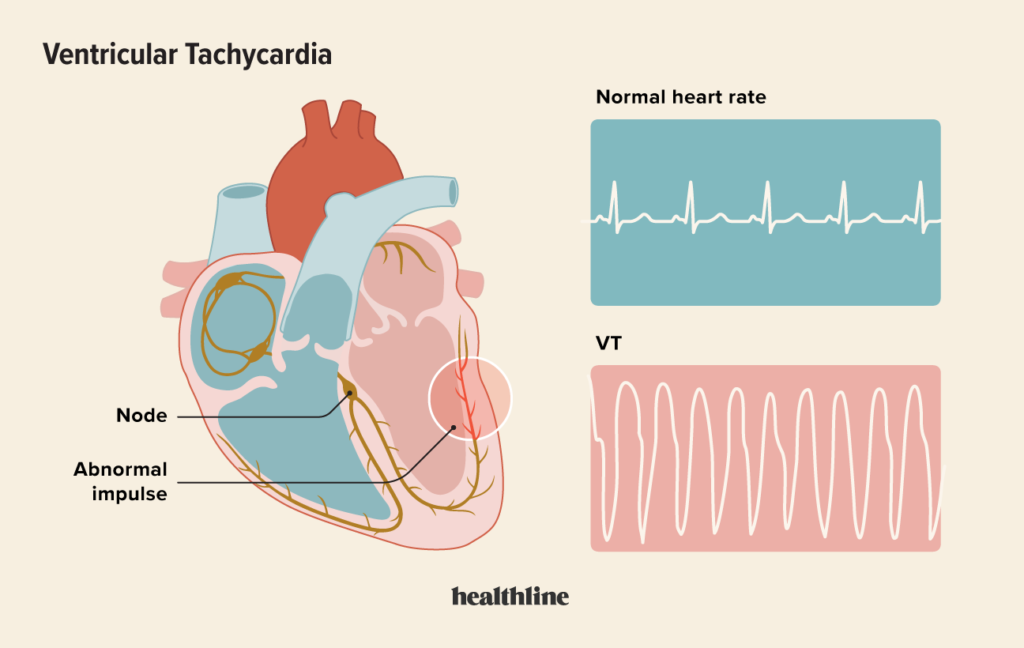
Proper ECG lead placement is paramount in obtaining clear and consistent readings of the heart’s electrical activity. Accurate placement ensures that the electrodes are positioned over the specific anatomical landmarks, allowing for optimal detection of electrical signals. This precision is crucial in diagnosing conditions like ventricular tachycardia and myocardial infarction, as inaccuracies in lead placement can lead to misinterpretation of results.
Basic Overview of ECG Leads
ECG leads are categorized into two main types: limb leads and chest leads. Limb leads, consisting of leads I, II, III, aVR, aVL, and aVF, monitor the electrical activity between various limb electrodes. On the other hand, chest leads, including V1 to V6, assess the electrical signals across the anterior, lateral, and inferior regions of the heart.
Each lead provides a unique perspective of the heart’s electrical conduction system, contributing to a comprehensive evaluation of cardiac function. Understanding the role of each lead and their corresponding anatomical locations is essential for accurate lead placement and precise interpretation of ECG findings.
By grasping the critical importance of precise ECG lead placement and familiarizing oneself with the fundamental principles of ECG leads, healthcare professionals can enhance the accuracy and reliability of ECG recordings, leading to improved diagnoses and better patient outcomes. Continued education and proficiency in ECG lead placement are vital in ensuring high-quality cardiac assessments and effective management of heart-related conditions.
Expert Strategies for Accurate ECG Lead Placement
When it comes to ensuring precise ECG lead placement, following expert strategies is paramount to obtaining accurate readings. This section covers the vital steps involved in preparing for lead placement, the correct techniques to follow during placement, and troubleshooting common errors that may arise.
Preparation Before Placement
Proper preparation is key to successful ECG lead placement. Before beginning the process, it is crucial to gather all the necessary equipment, including ECG electrodes, skin preparation supplies, and the ECG machine itself. Additionally, ensuring that the patient is comfortably positioned and adequately exposed for lead placement is essential for ease of access.
Once the equipment is ready, it is imperative to inspect the ECG electrodes for any defects that could compromise the accuracy of the readings. Checking the electrode sites for cleanliness and proper skin preparation is also crucial to ensure optimal electrode-skin contact for accurate signal transmission.
Correct Placement Techniques
Accurate ECG lead placement requires adherence to correct techniques to capture the electrical activity of the heart effectively. Understanding the anatomical landmarks for positioning the limb leads on the arms and legs as well as the precordial leads on the chest is fundamental to achieving accurate readings.
Correct lead placement techniques involve positioning the electrodes precisely according to standardized protocols. Each lead has a designated location on the body that corresponds to a specific view of the heart’s electrical activity. By following the recommended placement guidelines meticulously, healthcare professionals can obtain clear and reliable ECG tracings for interpretation.
Troubleshooting Common Placement Errors
Despite meticulous preparation and adherence to correct placement techniques, errors in lead placement can still occur. Common placement errors include electrode misplacement, inadequate skin preparation, and interference from external sources. Recognizing and rectifying these errors promptly is essential to prevent misinterpretation of the ECG results.
One effective troubleshooting technique for common placement errors is to systematically evaluate each lead for correct positioning and signal quality. If irregularities are detected, repositioning the electrodes, adjusting the skin contact, or eliminating sources of interference can help rectify the issue. Training and continuous education on proper lead placement techniques are also crucial for minimizing placement errors and optimizing ECG accuracy.
By focusing on thorough preparation, adherence to correct placement techniques, and proactive troubleshooting of errors, healthcare professionals can enhance the accuracy of ECG lead placement and ensure reliable interpretations of cardiac activity. For further insights on ECG interpretation, visit our article on ECG interpretation.
Specific Lead Placement Guidelines
When it comes to electrocardiogram (ECG) lead placement, precision is paramount in obtaining accurate readings for heart investigations. Understanding the specific guidelines for placing limb leads, chest leads, and augmented leads is essential for healthcare professionals to ensure reliable ECG results.
Limb Lead Placement
Limb lead placement plays a crucial role in capturing the electrical activity of the heart from different angles. The standard limb leads are placed on the limbs: right arm (RA), left arm (LA), and left leg (LL). Each lead provides a unique perspective of the heart’s electrical impulses.
To achieve accurate limb lead placement, follow these general guidelines:
| Lead | Placement |
|---|---|
| RA (Right Arm) | Right wrist or upper right arm |
| LA (Left Arm) | Left wrist or upper left arm |
| LL (Left Leg) | Lower left ribcage or upper left thigh |
Proper positioning of limb leads is essential for obtaining clear and consistent ECG tracings, facilitating accurate interpretation of the heart’s electrical activity.
Chest Lead Placement
Chest lead placement involves positioning electrodes on the chest to capture the electrical signals originating from different regions of the heart. Chest leads, also known as precordial leads, provide a comprehensive view of the heart’s activity in the frontal plane.
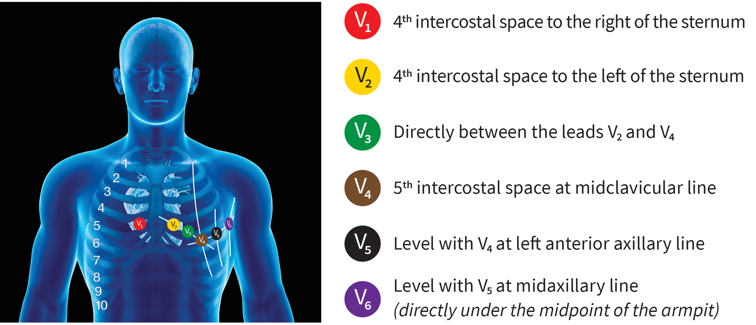
The standard chest lead positions include:
| Lead | Placement |
|---|---|
| V1 | Fourth intercostal space, right sternal border |
| V2 | Fourth intercostal space, left sternal border |
| V3 | Midway between V2 and V4 |
| V4 | Fifth intercostal space, midclavicular line |
| V5 | Anterior axillary line, same level as V4 |
| V6 | Mid-axillary line, same level as V4 and V5 |
Accurate placement of chest leads is crucial for recording consistent and reliable ECG waveforms, aiding in the diagnosis and management of various cardiac conditions.
Augmented Lead Placement
Augmented leads, including aVR, aVL, and aVF, provide additional perspectives on the heart’s electrical activity. These augmented leads are derived from the combination of limb leads to create a virtual viewpoint of the heart’s electrical axis.
The placement of augmented leads is as follows:
- aVR: Between the right arm and left leg leads.
- aVL: Between the left arm and left leg leads.
- aVF: Between the right arm and left arm leads.
Proper positioning of augmented leads ensures a comprehensive assessment of the heart’s electrical conduction system, aiding in the accurate interpretation of ECG waveforms.
By adhering to specific lead placement guidelines for limb leads, chest leads, and augmented leads, healthcare professionals can enhance the accuracy of ECG recordings, leading to precise diagnosis and effective management of cardiac conditions. For further insights into ECG interpretation, visit our article on ECG interpretation.
Enhancing Interpretation Through Accurate Lead Placement
When it comes to electrocardiography (ECG), the accuracy of lead placement plays a vital role in obtaining reliable and interpretable results. Proper lead placement not only ensures accurate recordings but also facilitates the correct interpretation of the heart’s electrical activity. This section will explore the impact of correct lead placement on ECG interpretation and the significance of ongoing education to enhance lead placement skills.
Impact of Correct Lead Placement on ECG Interpretation
Correct lead placement is essential for capturing the electrical signals of the heart accurately. Each lead has a specific orientation and location on the body, and deviations from standard placement can result in distorted ECG tracings. Misplaced leads can lead to misinterpretation of the ECG waveform, potentially masking or mimicking cardiac abnormalities.
By placing the ECG leads precisely according to established guidelines, healthcare professionals can create an ECG recording that faithfully represents the heart’s electrical activity. This accurate depiction is crucial for diagnosing various cardiac conditions, such as ventricular tachycardia and myocardial infarction, and monitoring changes in the heart’s rhythm over time.
Continual Education for Improved Placement Skills
Continuous education and training are key components in enhancing lead placement skills among healthcare practitioners. Regular review and reinforcement of proper lead placement techniques help to maintain proficiency and accuracy in performing ECGs. Training sessions, workshops, and refresher courses can provide healthcare professionals with the opportunity to refine their skills and stay updated on the latest guidelines and best practices in lead placement.
Furthermore, incorporating hands-on practice and interactive learning activities can further solidify understanding and competence in ECG lead placement. By encouraging a culture of continual learning and improvement, healthcare providers can ensure that ECGs are conducted with precision and consistency, ultimately leading to more reliable interpretations and better patient care outcomes.
In the realm of ECG interpretation, the accuracy and consistency of lead placement are paramount. Healthcare professionals must prioritize proper lead placement techniques and commit to ongoing education and skill development to optimize the quality and reliability of ECG recordings. By upholding high standards in lead placement practices, healthcare providers can confidently interpret ECG results and make informed clinical decisions for their patients.